Option Premium


Dive into the world of trading as we unpack the blueprint of an option premium and its significant influence on the stock market. This concise guide will simplify the trading jargon and provide valuable insights to empower your investment decisions.
What is Option Premium?
Option premium is a term used in the stock market. It is the price paid by an investor for an options contract, which grants them the right to buy or sell a stock at a specific price within a set timeframe. The premium price is influenced by factors such as the stock’s current price, the strike price of the option, the time remaining till expiry, and the volatility of the stock. The option premium can also change depending on the market conditions. However, once an option premium is paid, it is not refundable.
What are the different types of options?
Options in trading refer to a contract that provides the right to buy or sell assets. The two main types are call and put options. A call option allows the holder to buy an asset at a specified price within a certain period. Conversely, a put option grants the holder the right to sell an asset at a preset price. There are also American and European options. These options provide different opportunities depending on market conditions and the trader’s strategy.
What are factors infulencing option premium?
Option premium, the price paid by the buyer to the seller for the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a certain period, is influenced by multiple factors that traders and investors need to consider when evaluating options.
Factors influencing option premium:
- Intrinsic Value: This is the portion of the option premium that is based on the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the option’s strike price.
- Time Value: Time value, also known as extrinsic value, represents the portion of the option premium that is attributable to the time remaining until the option’s expiration.
- Volatility: Volatility refers to the degree of fluctuation in the price of the underlying asset. Higher volatility implies greater uncertainty about the future price movements of the asset, leading to an increase in the option premium.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates can impact option premiums, particularly for options with longer time horizons. Higher interest rates tend to increase option premiums because they increase the present value of future cash flows associated with the option.
- Dividends: For options on dividend-paying stocks, the timing and amount of dividends can affect option premiums. When a stock pays a dividend, the stock price typically decreases by the dividend amount, which can influence the option’s intrinsic value.
Understanding these factors and their impact on option premiums is essential for traders and investors to make informed decisions about option trading strategies. By considering these variables, market participants can assess the risk and potential return associated with various options and optimize their trading approach accordingly.
What is option greek?
Option Greek refers to the specific risk factors that affect the price of options in the stock market. They are statistical metrics used to measure the sensitivity of an option’s price to various factors. These factors include changes in the price of underlying assets, time to expiration, volatility, and the risk-free interest rate. The most common Option Greeks are Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho. Traders use these Greeks to manage their risk, optimize their portfolio, and make better trading decisions.
What is impact of option greeks in option premium?
Option Greeks significantly impact the premium of options in option trading. They represent the sensitivity of the option’s price to various factors. Delta, one of the Greeks, measures how the option’s price changes as the price of the underlying asset changes. Theta, on the other hand, deals with the time decay effect on options. It indicates how the price of an option decreases over time. These Greeks influence the option’s premium due to variations in the underlying asset’s price, time decay, volatility, and change in Delta.

The following are the different Option Greeks in the market:
Delta (Δ) – It calculates the extent to which option premium would change because of a small change in the underlying price. Delta measures the difference in the value of premium to change in the value of underlying. For a call option, Delta’s value varies between 0 and 1, and for a Put option, the value of Delta varies between -1 and 0.
Gamma (Γ)– It calculates the extent to which Delta would change because of the change in the underlying value. It defines the speed with which option would become in-the-money or out-of-the-money due to fluctuations in the underlying price.
Theta (Θ) – Theta is an essential factor in deciding option pricing. Time is an ingredient in determining the premium for a particular strike price. Time decay reduces the option Premium as it nears expiry. Theta is the time decay factor, i.e., the rate at which option premium loses value over time as it is near expiry.
Vega (v) – Vega, as a greek, is sensitive to the current volatility. Volatility is the rate of change because of the changes in market volatility. Vega signifies the difference in the value of an option for a 1% change in the underlying asset price. Higher the volatility of the underlying asset, the more expensive it is to buy the option.
Rho (p) – Rho is a metric used for assessing the sensitivity of an option premium to changes in the risk-free interest rate.
How do you calculate option premium?
Option premium, in the context of option trading, is calculated using specific models. The factors used in these models include the stock’s current price, the option’s exercise price, the time to expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. The most common model is Black-Scholes. It’s a mathematical formula that uses these factors to determine the price of both put and call options. The result of the calculation gives the cost, or premium, the buyer needs to pay the seller for the option.
Premium = Time Value + Intrinsic Value
The intrinsic value is determined by the difference between the current trading price and the strike price. Only in-the-money options have intrinsic value. Intrinsic value can be computed for in-the-money options by taking the difference between the strike price and the current trading price.
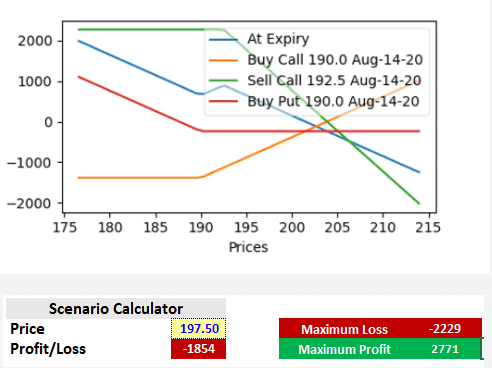
The time value is dependent upon the length of time remaining to exercise the option. The time value of an option decreases as its expiration date approaches and becomes worthless after that date. This phenomenon is known as time decay.
What are various models of option pricing?
Option pricing models, essential in option trading, calculate theoretical option prices. The Black-Scholes model, applicable to European options, considers factors like current stock price, strike price, time to expiration, and volatility. The Binomial model is for American options, using a tree structure to model stock price changes. Monte Carlo simulation, the most flexible but complex, employs random sampling and statistical analysis to estimate option prices by accommodating various assumptions and changing variables.
What is Black -Scholes model? How does it work?
The Black-Scholes model revolutionized options pricing by providing a framework for understanding and quantifying the value of financial derivatives.
Key factors influencing the model:
- Current Stock Price: This is the price of the underlying asset, such as a stock, at the time of the option’s valuation. It serves as a starting point for the model’s calculations.
- Option’s Strike Price: The strike price, also known as the exercise price, is the price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. It represents the price level at which the option becomes valuable.
- Time Until Expiry: This refers to the length of time remaining until the option contract expires. The longer the time until expiry, the greater the potential for the option to move in value, and thus, the higher the option’s price.
- Risk-Free Interest Rate: This is the theoretical rate of return on an investment with zero risk of financial loss.
- Stock Volatility: Volatility measures the degree of variation in the price of the underlying asset. Higher volatility implies greater uncertainty about the future price movements of the stock.
By inputting these variables into the Black-Scholes formula, traders and investors can calculate the theoretical price of an option.
What is the Binomial model ? How does it work?
The binomial model is a powerful tool in finance for pricing options and understanding their value dynamics over time. At its core, the model relies on a simple yet effective concept: the idea that an asset’s price can only move in one of two directions.
Here’s how the binomial model works:
- Time Segmentation: The model breaks down time into discrete intervals, typically represented by steps or periods.
- Price Movement Assumption: At each time step, the model assumes that the price of the underlying asset can either increase by a certain factor or decrease by another factor
- Constructing the Binomial Tree: Using these price movement factors, the model constructs a binomial tree, starting from the current price of the asset at the initial time step Each node in the tree represents a possible price of the asset at a specific point in time.
- Option Valuation: The model then evaluates the option’s payoff at each node of the tree. This involves calculating the option’s intrinsic value at each node, based on whether the option is a call or put option.
- Risk-Neutral Probability: To calculate the option’s expected value at each node, the model uses the concept of risk-neutral probability. This probability reflects the likelihood of upward or downward movements in the asset’s price, adjusted for the risk-free rate and the time interval.
- Backward Induction: Starting from the final time step and working backward through the tree, the model calculates the option’s value at each preceding node by discounting the expected payoff at that node to the present time.
The binomial tree model evaluates option values at each node, offering insights into future price ranges and option values.
What is the Monte Carlo? How does it work?
Monte Carlo simulation is a versatile computational technique used in various fields, including option trading in stock markets. Its application in finance, particularly in pricing options, offers a flexible and powerful approach to account for risk and uncertainty.
Here’s a deeper dive into how Monte Carlo simulation works in option trading:
- Random Sampling: Monte Carlo simulation begins by generating a large number of random price path scenarios for the underlying asset. These scenarios represent possible future trajectories of the asset’s price.
- Option Payoff Estimation: Once the price path scenarios are generated, the next step is to evaluate the option’s payoff for each scenario.
- Statistical Analysis: After calculating the payoffs for all scenarios, statistical techniques are applied to analyze the distribution of option payoffs. This includes calculating summary statistics such as mean, median, standard deviation, and quantiles.
- Risk Assessment and Decision-Making: Monte Carlo simulation enables traders to understand the risk-return profile of options more comprehensively. By simulating a wide range of possible market scenarios, traders can assess the likelihood of various outcomes and make more informed decisions
- Complex Problem Solving: One of the key advantages of Monte Carlo simulation is its ability to handle complex & multi-dimensional problems in option trading. It can accommodate various sources of uncertainty and model interactions between different market variables more realistically than traditional analytical methods.
Overall, Monte Carlo simulation is a valuable tool in option trading, offering a systematic approach to quantify risk.. Its flexibility and robustness make it well-suited for addressing the challenges of dynamic and unpredictable financial markets.
Summary
Option premium, the price paid for the right to purchase or sell an asset at a specific cost within a certain time period, is influenced by factors like the current asset price, time until expiration, volatility, interest rates, and dividends. Two significant types of options are call and put options, and these premiums impact trader’s strategies based on market conditions. Option Greeks, attributes like Delta and Vega that indicate changing market factors, also play a significant role in determining option premiums. This premium can be calculated using models like the Black-Scholes model, the Binomial model, and the Monte Carlo simulation, which consider factors like asset price, strike price, and expiration time.
Get Market data in Excel easy to use formulas
- Real-time Live Streaming Option Prices & Greeks in your Excel
- Historical (intraday) Options data in your Excel
- All US Stocks and Index options are included
- Real-time prices and data on underlying stocks and indices
- Works on Windows, MAC or even online
- Implement MarketXLS formulas in your Excel sheets and make them come alive
- Save hours of time, streamline your option trading workflows
- Easy to use with formulas and pre-made templates

I invite you to book a demo with me or my team to save time, enhance your investment research, and streamline your workflows.